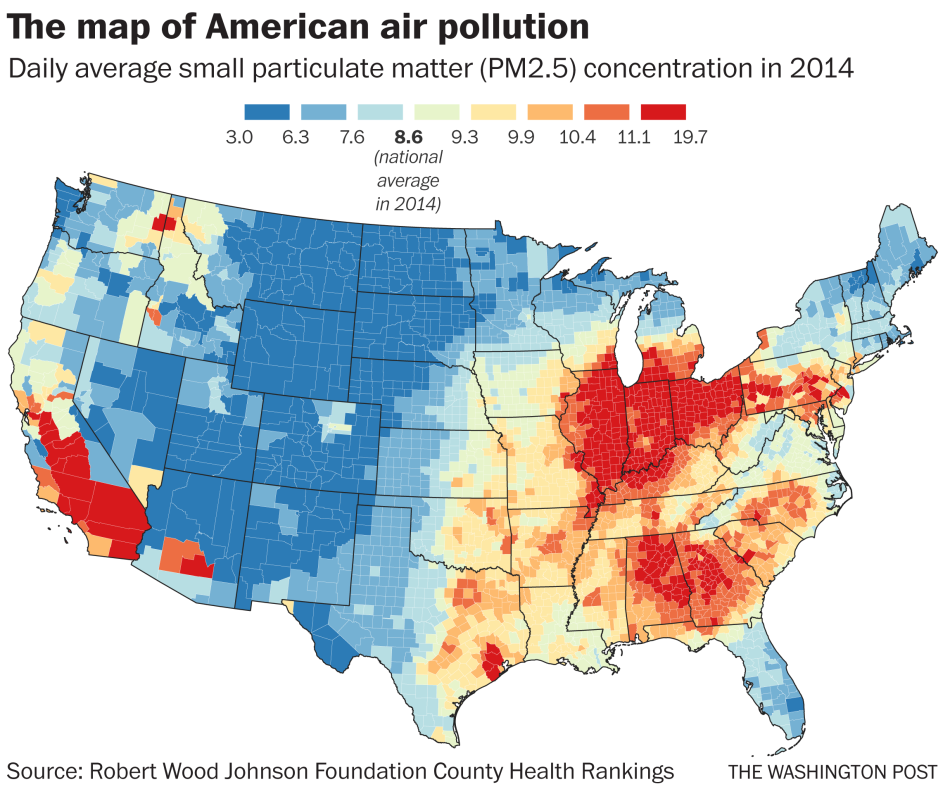
Tennessee is faced with extreme pollution issues with its diverse landscapes, cities like Memphis and Murfreesboro, and plenty of biodiversity.
These problems have their roots in industrial activity, transportation, agriculture and extensive urbanization. Pollution in Tennessee is not only damaging to the state’s ecosystem, but also to its people and its wildlife. So let’s examine some important pollution issues in Tennessee, what is behind the pollution and what might be done to help.
Air Pollution
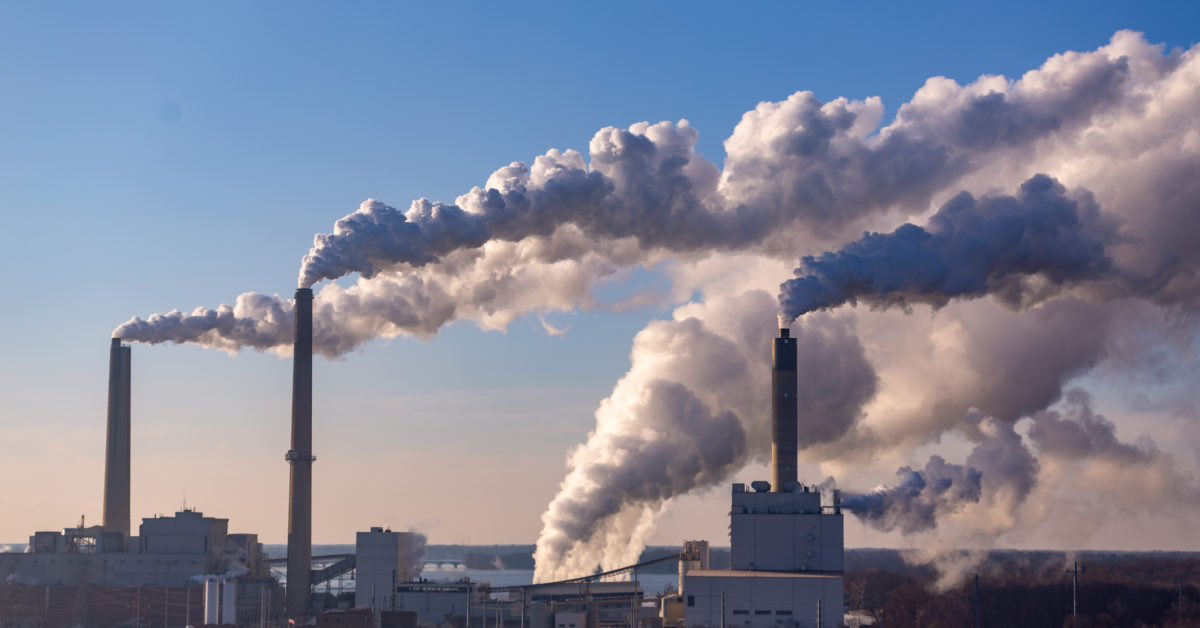
In Tennessee air quality is a significant issue, particularly in urbanized areas like Nashville, Knoxville and Memphis. Tennessee has long struggled with elevated levels of air pollutants like ozone or particulate matter, as well as nitrogen oxides (NOx), largely from vehicles, industrial activity and power generation.
Transportation remains one of the largest sources of air pollution in Tennessee. With the state’s growing population and more vehicles on the road, the result is more carbon monoxide (CO), sulfur dioxide (SO2) and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in the air. These pollutants combine in the atmosphere to create ground-level ozone, a key ingredient of smog, which can cause respiratory problems and worsen conditions like asthma and bronchitis.
Then there’s the reliance on fossil fuel-powered plants that have historically driven air pollution in Tennessee.
Though the state has taken subsequent steps to move away from fossil fuel combustion toward cleaner sources, coal-fired plants and industrial facilities continue to release greenhouse gases and other pollutants there. The Tennessee Valley Authority (TVA) has made progress in reducing emissions, including phasing out coal-fired units and ramping up investments in renewable energy, but challenges remained.
Water Pollution
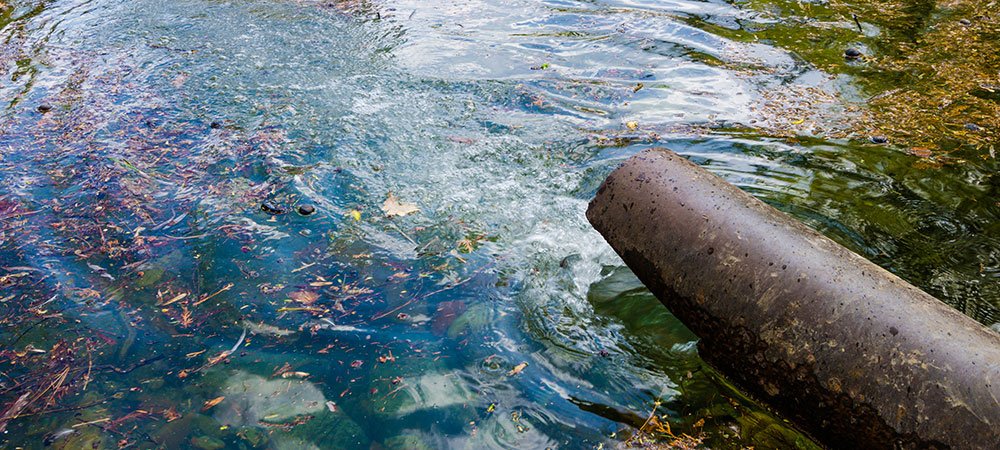
Tennessee has an extensive network of rivers, streams and lakes, including the Tennessee River, one of the state’s most important sources of water. It is sad to note that water contamination is a major problem. Agricultural runoff, urban stormwater, industrial discharges and outdated wastewater infrastructure all contribute to the pollution of these bodies of water.
Water pollution in Tennessee is mostly due to agriculture. Fertilizers, pesticides and animal wastes from farms commonly wash into nearby creeks and rivers with rain, adding high amounts of nitrogen and phosphorus. These nutrients can also cause harmful algal blooms, which suck oxygen from the water and can endanger aquatic ecosystems.
Urban stormwater runoff gives headaches, too. Urban growth leads to an increased amount of impervious surfaces (e.g., roads, parking lots) that prevents water from filtering naturally through the soil. Stormwater transports toxicants such as oil, grease, heavy metals, and litter to streams and rivers. And there are many wastewater treatment plants in Tennessee that are overwhelmed by growth and have periodic overflows of untreated waste into rivers.
Industrial pollution also poses a concern. Industries near water bodies may also flow chemicals and heavy toxicity in the environment. For example, the contamination of the Holston River near Kingsport, Tennessee, with industrial chemicals shows the need for we can enforce environmental regulations more strictly.
Soil Pollution
In Tennessee, soil contamination is more commonly associated with industrial activities, illegal dumping and agricultural practices.
Heavy metals, petroleum products, and pesticides are some of the hazardous substances that can build up in the soil and endanger public health and the environment. In some places, former factories, known as brownfields, are left tainted and unusable until expensive cleanups are completed and all the junk is discarded with dumpster rentals.
Tennessee’s rural areas are especially susceptible to illegal dumping. Incorrect disposal of waste (like chemicals or construction debris) can cause long-term damage to soil and pollution of the water table.
Wildlife and Ecosystem Impact
The effects of pollution can be felt throughout Tennessee’s ecosystems. Many endangered and threatened species, including freshwater mussels and fish, are found in the state. Aquatic habitats have suffered from water pollution, especially sedimentation and chemical runoff. Air pollution can also have detrimental effects on forests by harming tree health and growth.
Addressing Pollution
Pollution prevention efforts in Tennessee include regulation, education and new technology. The Tennessee Department of Environment and Conservation (TDEC) is primarily responsible for monitoring and enforcing environmental requirements. Efforts like watershed protection programs and air quality monitoring have helped reduce pollution.
It is also important to be involved in the community. At the same time, groups, such as the Tennessee Environmental Council, focus on awareness and sustainability. These are actions residents can take, like cutting down on waste, using less energy and advocating for clean transportation options.
Long-term, these are climate investments — renewable energy development, upgrading wastewater treatment plants, efficient dumpster rental services and sustainable agricultural practices — must be Tennessee’s path toward good environmental health. The state can protect its natural resources and the well-being of all Tennesseans by working together on our pollution problems.